Most of the languages are primarily oral with little available in written form. The languages of Africa break down into four large families (phyla) the four continental language families are:
- Niger-Congo
- Afroasiatic
- Nilo-Saharan
- Khoisan
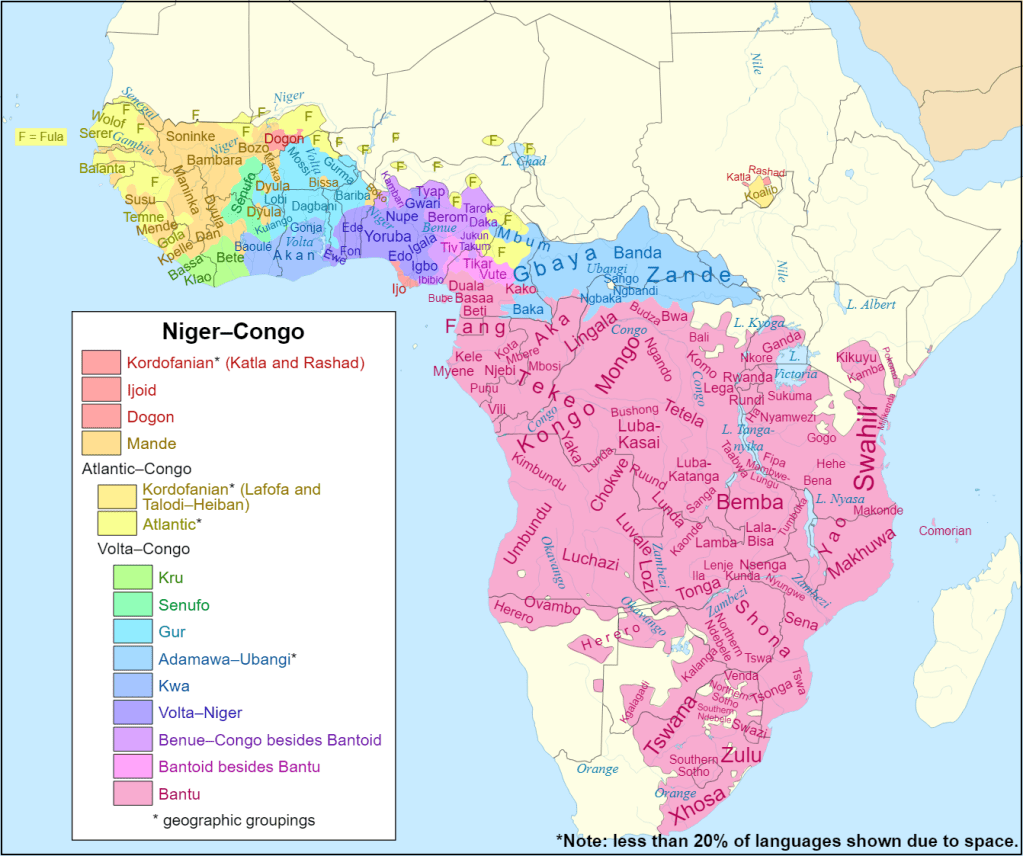
Niger-Congo
The largest language family of the four and contains between 1350-1650 languages. The most widely spoken languages of Africa, Swahili (200 million), Yoruba (45 million), Igbo (30 million), and Fula (35 million) all belong to the Niger-Congo family (Harvard, 2024).
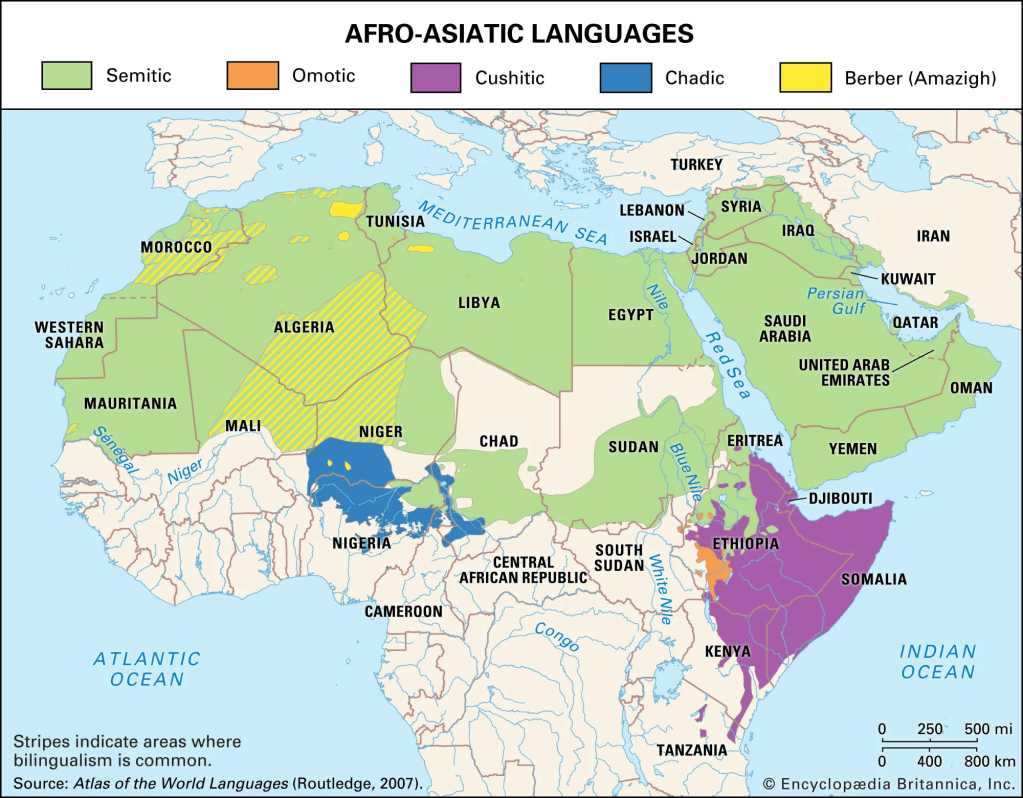
Afroasiatic
The next largest is the Afroasiatic language group with about 200-300 languages. Mostly found in the Northern regions of Africa, including northern Nigeria (Hausa), southern Niger, Somalia, Ethiopia, Eritrea, and in the North African countries of Morocco, Algeria and Tunisia.
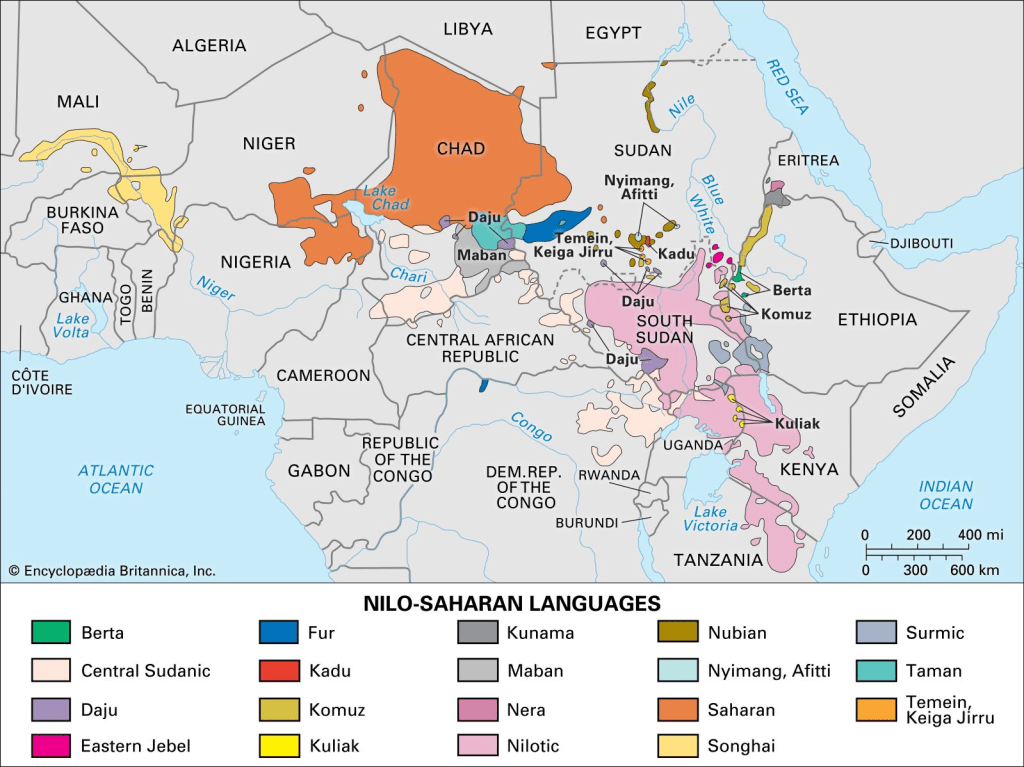
Nilo-Saharan
Next in size is the Nilo-Saharan family with about 80 languages. These occupy Eastern Africa and the North Eastern region of Africa, namely Uganda, Tanzania, Kenya, Chad and the Sudan.
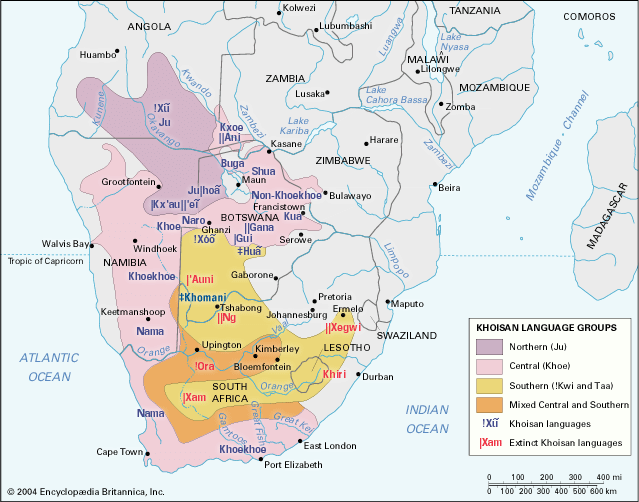
Khoisan
Last but not least is the Khoisan family with between 40 – 70 members. Believed to be the oldest of the four language families, it is the smallest of the four and is found mainly in Southern Africa.
References:
Introduction to African Languages. (n.d.). Alp.fas.harvard.edu. https://alp.fas.harvard.edu/introduction-african-languages#:~:text=The%20most%20widely%20spoken%20languages
Leave a comment