End of the First French Colonial Empire
In 1803, France sold its extensive North American colony to the United States, in a transaction commonly known as the ‘Louisiana Purchase’, marking the substantial decline of the First French Colonial Empire. By the mid 19th century, France had lost many of its colonial possessions. Most of which were lost to the United Kingdom such as its ‘sugar islands’ in the Caribbean and its colonies in India. However, France would embark on new colonial conquests after the Napoleonic Wars (WorldAtlas, 2021).

France’s Invasion of Algeria
The beginning of the Second French Colonial Empire can be marked by the France’s invasion of Algeria in 1830. It took the French 17 years to conquer the country but by the late 19th century, France had established control in Algeria and huge territories in coastal West Africa.
On the 16th of May 1830, King Charles X ordered a fleet comprising of over 100 ships and 37000 men to depart from Toulon, France. After the fleet landed on the morning of 14 June 1830, many French soldiers found themselves being ambushed by Algerian scouts as they were disembarking.

Battle of Staoueli
Hussein Dey’s three Beys (chieftains), from Oran, Titteri and Medea had answered the call to arms and began gathering forces in a large camp on the nearby plateau of Staoueli. On the 19th of June, the Algerian forces attacked the two French divisions that had already disembarked. However, this was a colossal failure as French artillery fire forced the Algerians to retreat. By midday, the French had captured the camp, pillaging weapons, food and livestock as they went (wikipedia).
Siege of Bordj Moulay Hassan Fortress
On the 29th of June, French forces approached the Bordj Moulay Hassan Fortress, the last line of defense between them and Algiers (capital of Algeria). They began digging trenches in preparation for the siege and by July 3rd, the French had brought all of their artillery.
In the early morning of July 4th, French general De la Hitte ordered all French batteries to open fire; in response, the defenders returned fire and a cannonade ensued. The entire fortress was devastated within a few hours before the remaining Algerians survivors fled, only half of the 2000 initial Algerian men made it out.
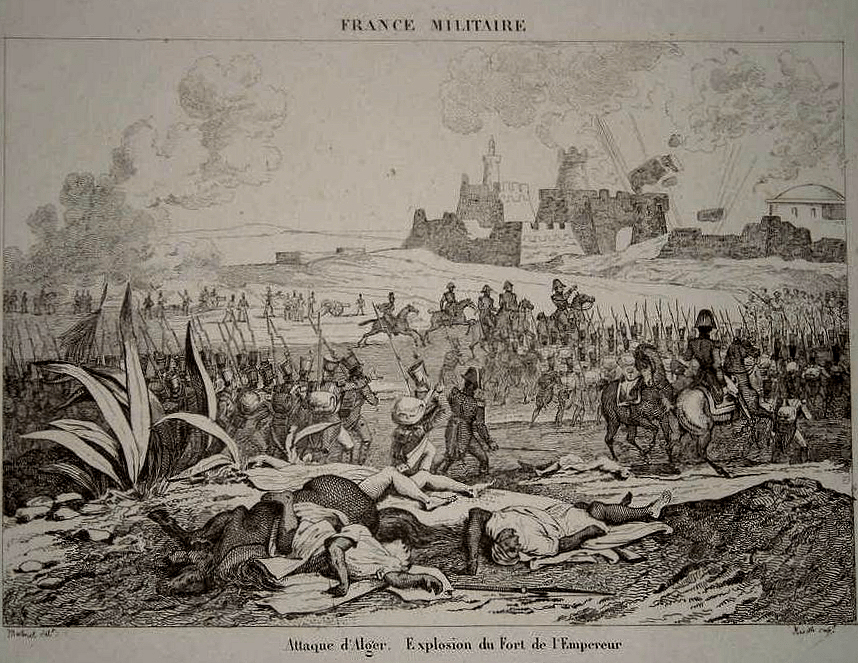
Capitulation of Algiers
With the fortress completely destroyed, the French began advancing towards the city of Algiers and exchanged fire with the citadel. A while later, two delegates from Hussein Dey negotiated an armistice. The French demanded control of the city, its fleet and the treasury as well as the departure of the Turks and in return, they would not pillage any houses.
A few days later, Hussein Dey and his family were exiled to Naples, where he stayed for three years and died in Alexandria in 1838.
Thus marked the beginning of French colonialism in Africa, with Algeria suffering even more bloodshed up till its independence in 1962.
References
Shvili, J. (2021, December). Second French Colonial Empire. WorldAtlas; WorldAtlas. https://www.worldatlas.com/geography/second-french-colonial-empire.html#:~:text=The%20beginning%20of%20the%20Second
French conquest of Algeria. (2023, March 10). Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/French_conquest_of_Algeria#:~:text=In%201827%2C%20an%20argument%20between
Wikipedia Contributors. (2024, June 14). Invasion of Algiers (1830). Wikipedia; Wikimedia Foundation. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Invasion_of_Algiers_(1830)#
Leave a comment